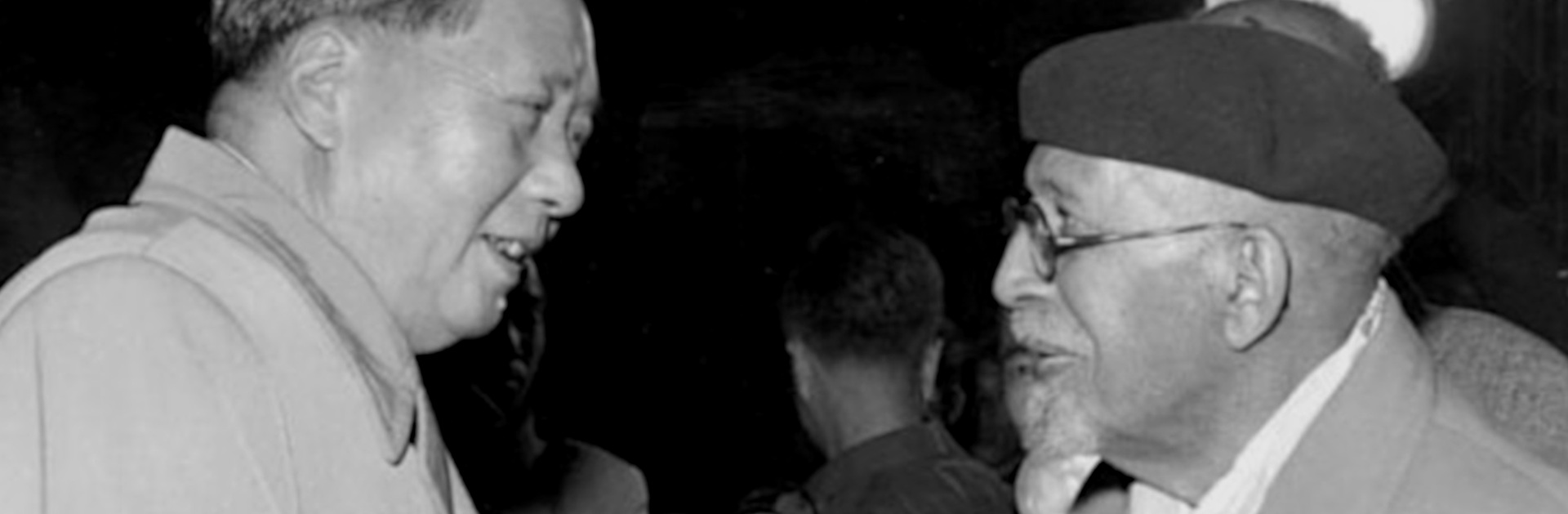
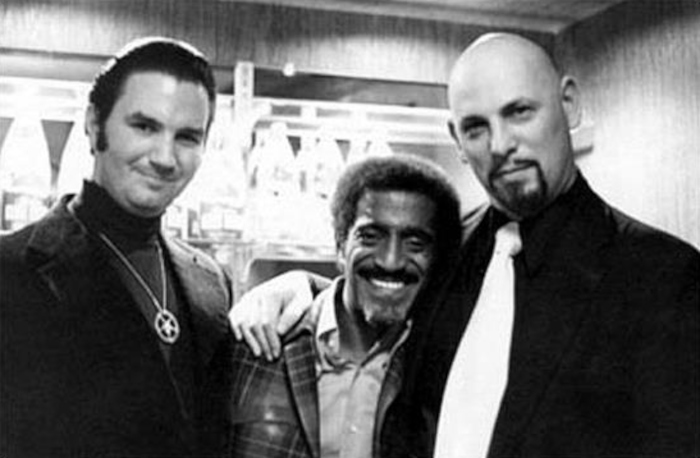
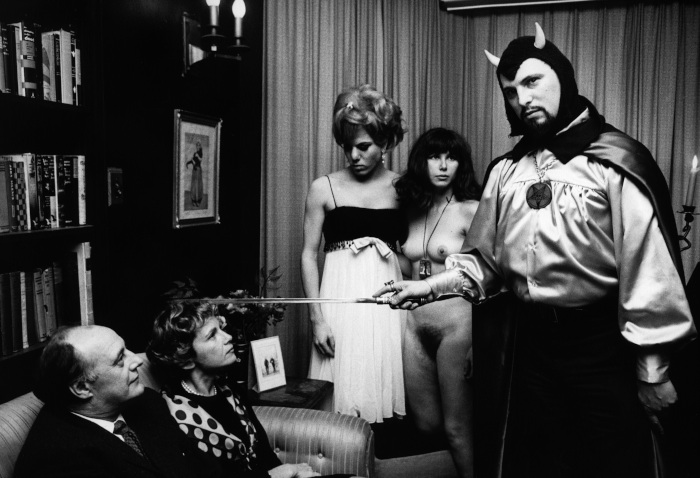
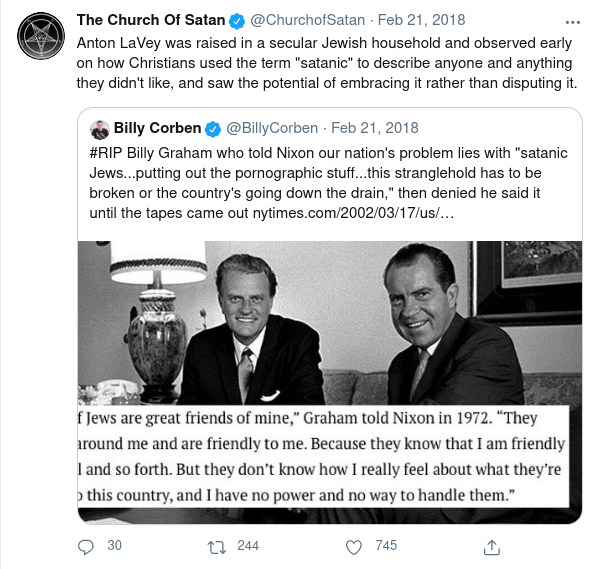
Mass murderer Mao Zedong and NAACP co-founder W. E. B. Du Bois.
NAACP
From Segregation to Integration and then Miscegenation, the secretive Communist, trans-racial Agenda of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People.
- Introduction
- W. E. B. Du Bois
- Moorfield Storey
- Henry Moskowitz
- Robert Franklin Williams
- Spingarn Brothers
- Oswald Garrison Villard
- Miscegenation Melting Pot
- Conclusion
“I can conceive of no greater calamity than the assimilation of the Negro into our social and political life as our equal.”.
Introduction
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) is a crypto-Communist civil rights organisation in the United States, formed in 1909 as a bi-racial endeavour to advance justice for African Americans by a group including W. E. B. Du Bois, Mary White Ovington, Moorfield Storey and Ida B. Wells. Today the NAACP promotes a race-first agenda that seeks to elevate minorities in school, politics, and the workplace-based only on skin-colour.
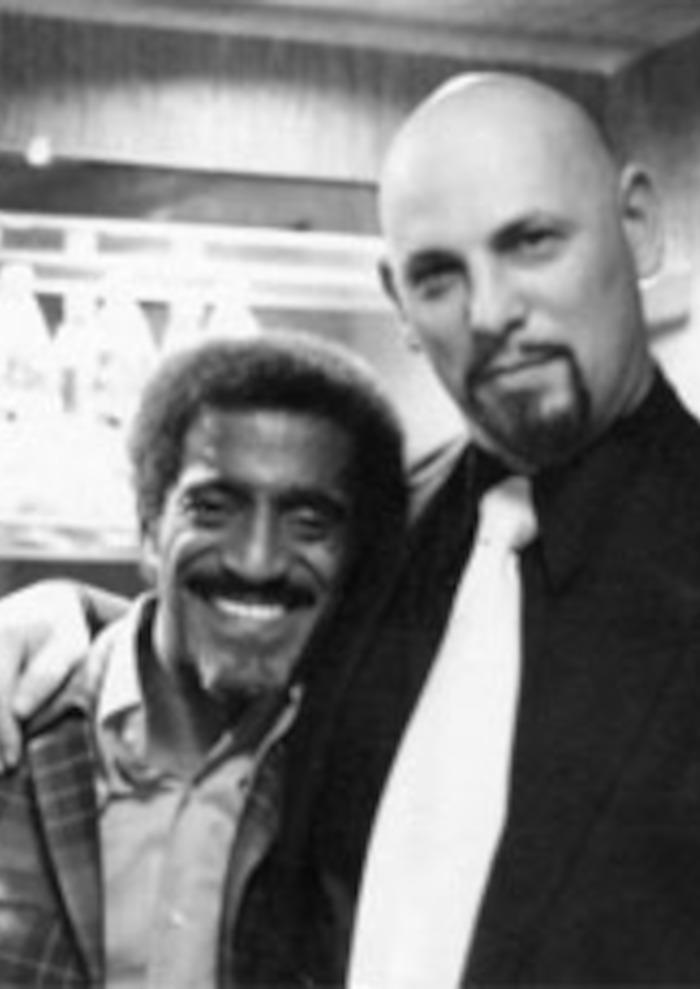


“Roy Wilkins of the NAACP played a role in the Civil Rights Movement (March on Washington with Sammy Davis Jr, later member of Anton LaVey's Church of Satan).”.


“God is on your side? Is He a Conservative? The Devil's on my side, he's a good Communist.”
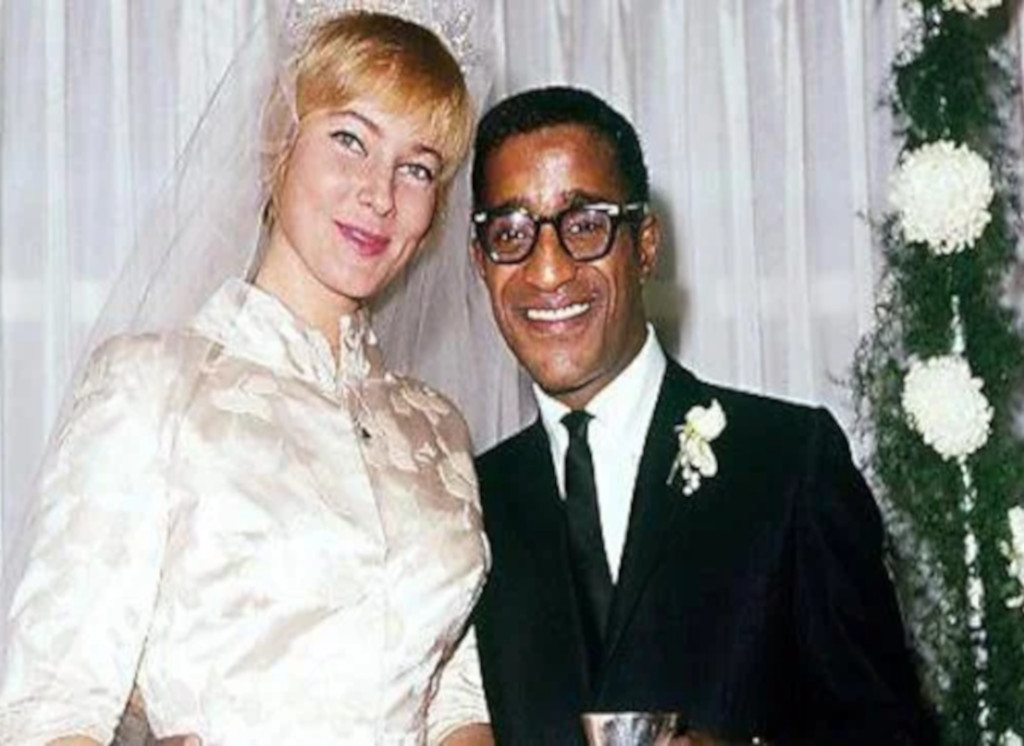
According to Davis' daughter, President Kennedy refused to let her father perform after he married Swedish actress Mary Britt. At that time interracial marriage was forbidden by law in 31 U.S. states.


The NAACP advocates for affirmative action programs that regularly discriminate against both white and Asian Americans. The NAACP over the century has had historical links with Communism. In 1938, NAACP members participated in the Soviet-controlled World Youth Congress. During the 1940s, the NAACP was affiliated with the Communist-involved World Federation of Democratic Youth. In 1946, the NAACP supported the establishment of the Communist-dominated Progressive Party.
W. E. B. Du Bois
William Edward Burghardt Du Bois was born mixed-race during the year of 1868 in Massachusetts to Alfred and Mary Silvina (née Burghardt) Du Bois. Mary Silvina Burghardt's family was descended from Dutch, African and English ancestors. Du Bois, as alumni of the New School, was one of the founders of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) in 1909.
In May 1909, Du Bois attended the National Negro Conference in New York. The meeting led to the creation of the National Negro Committee, chaired by Oswald Villard, and dedicated to campaigning for civil rights, equal voting rights, and equal educational opportunities. The following spring, in 1910, at the second National Negro Conference, the attendees created the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP).
At Du Bois's suggestion, the word “coloured”, rather than “black”, was used to include "dark-skinned people everywhere”.
“[anti-miscegenation] laws leave the colored girls absolutely helpless for the lust of white men. It reduces coloured women in the eyes of the law to the position of dogs. As low as the white girl falls, she can compel her seducer to marry her ... We must kill [anti-miscegenation laws] not because we are anxious to marry the white men's sisters, but because we are determined that white men will leave our sisters alone.”.
NAACP leaders offered Du Bois the position of Director of Publicity and Research. He accepted the job in the summer of 1910 and moved to New York after resigning from Atlanta University. His primary duty was editing the NAACP's monthly magazine, which he named The Crisis. Typical articles in the early editions included one that inveighed against the dishonesty and parochialism of black churches, and one that discussed the Afrocentric origins of Egyptian civilisation.


A rivalry emerged in 1931 between the NAACP and the Communist Party when the Communists responded quickly and effectively to support the Scottsboro Boys, nine African-American youth arrested in 1931 in Alabama for rape. Du Bois and the NAACP felt that the case would not be beneficial to their cause, so they chose to let the Communist Party organise the defence efforts. After arriving at his new professorship in Atlanta, Du Bois wrote a series of articles generally supportive of Marxism. The rift with the NAACP grew larger in 1934 when Du Bois reversed his stance on segregation, stating that “separate but equal” was an acceptable goal for African Americans.
“…particularly in the South, there was being put into force one of the most extraordinary experiments of Marxism that the world, before the Russian Revolution, had seen.”.
The NAACP leadership was stunned and asked Du Bois to retract his statement, but he refused, and the dispute led to Du Bois's resignation from the NAACP. Du Bois was a member of the three-person delegation from the NAACP that attended the 1945 conference in San Francisco at which the United Nations was established. The NAACP delegation wanted the United Nations to endorse racial equality and to bring an end to the colonial era. The NAACP proposal received support from China, Russia and India, but it was virtually ignored by the other major powers, and the NAACP proposals were not included in the United Nations charter.
“As one of the despised minorities of man, he first set Russia on the road to conquer race prejudice and make one nation out of its 140 groups without destroying their individuality.”.


“I believe in Communism. I mean, by Communism, a planned way of life in the production of wealth and work designed for building a state whose object is the highest welfare of its people and not merely the profit of a part.”.
Du Bois continued to believe that capitalism was the primary culprit responsible for the subjugation of coloured people around the world, and therefore — although he recognised the faults of the Soviet Union — he continued to uphold Communism as a possible solution to racial problems. In the words of biographer David Lewis, Du Bois did not endorse Communism for its own sake, but did so because “the enemies of his enemies were his friends”.

In 1953, Du Bois revised The Souls of Black Folk for its fiftieth anniversary; it was the only time he changed its text. He made fewer than ten edits, and two of them were to this passage, which he changed from “The Jew is the heir of the slave-baron … and the Jew fell heir.” to “Immigrants are heirs of the slave-baron … and foreigners fell heir.” He explained his changes in a paragraph he asked his publisher to add at the end of the chapter:
“In the foregoing chapter, “Jews” have been mentioned five times, and the late Jacob Schiff once complained that this gave an impression of anti-Semitism. This at the time I stoutly denied; but as I read the passages again in the light of subsequent history, I see how I laid myself open to this possible misapprehension”.
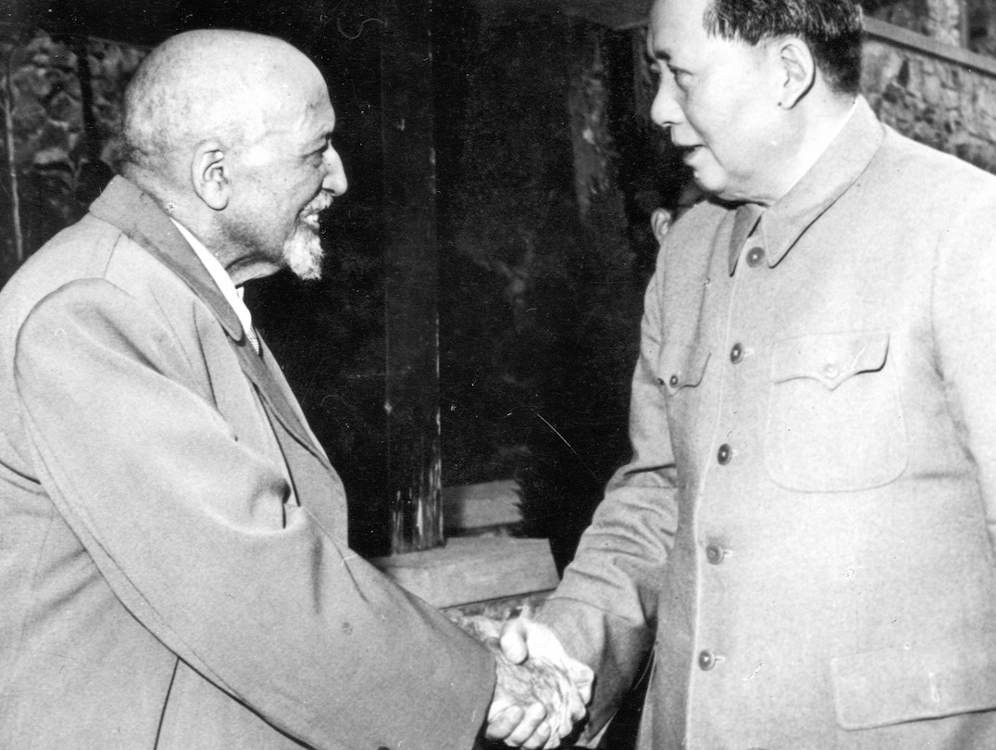
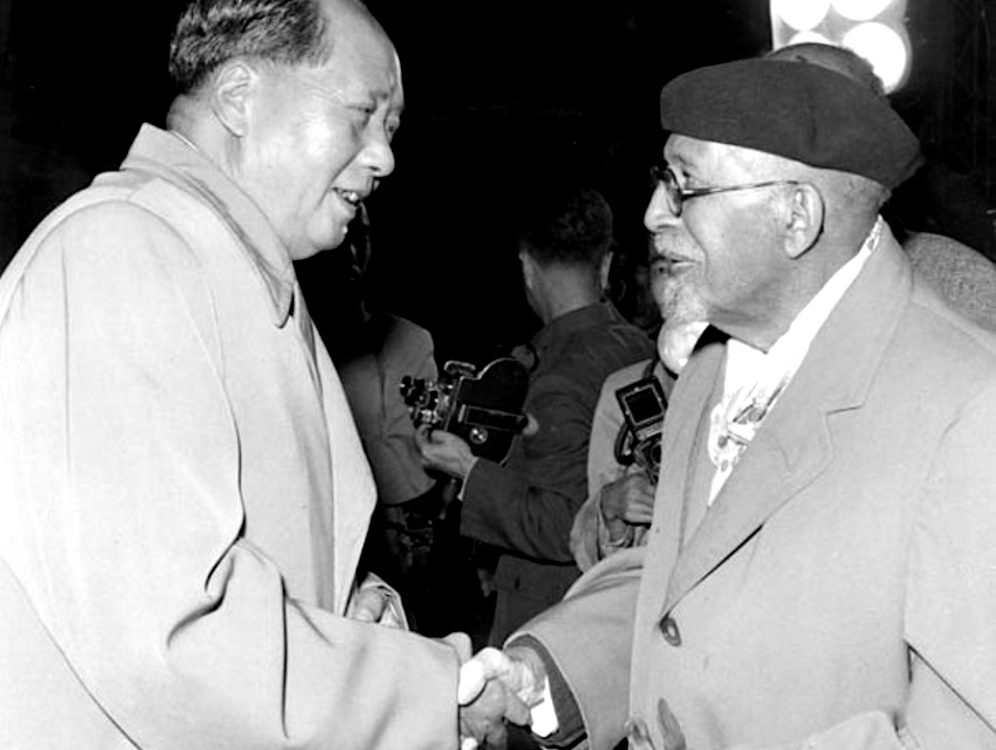
In 1958, Du Bois with his second wife, Shirley Graham Du Bois visited Russia and China. In both countries, he was celebrated. Du Bois later wrote approvingly of the conditions in both countries. In October 1961, at the age of 93 he joined the Communist Party. He also asked Herbert Aptheker, a Communist and historian of African-American history, to be his literary executor.
Du Bois helped further Mao’s goals for an Afro-Asian alliance. On February 23, 1958, he addressed a crowd of thousands at Peking University, which Peking Radio broadcast around the world. Speaking directly to African leaders across the Indian Ocean, Du Bois proclaimed:
“Africa arise, and stand straight…Turn from the west and your slavery and humiliation for the last 500 years China is flesh of your flesh and blood of your blood.”.
Graham Du Bois recalled that as Mao and W. E. B. Du Bois went for a stroll among the cherry trees:
“back to us came the sound of laughter…as carefree and wholehearted as that of a couple of schoolboys.”.
The W.E.B. Du Bois Clubs of America was a national youth organisation sponsored by the Communist Party USA (CPUSA) and launched at a national convention held in San Francisco in June 1964. The organisation was active in the American student movement of the 1960s and maintained a prominent presence on several college campuses, including Columbia University in New York City and the University of California in Berkeley. The organisation became dissolved by decision of the CPUSA in February 1970 and succeeded by a new organisation known as the Young Workers Liberation League.

As the 1960s came to a close, the Du Bois Clubs were rendered virtually obsolete by various radical youth organisations of the so-called "New Left," including in particular the Students for a Democratic Society. Membership in the Du Bois Clubs plummeted to less than 100, prompting the Communist Party to rethink its commitment to a formally non-party mass organisation of youth. However, according to COINTELPRO papers, the Counterintelligence Program claims to have been instrumental in the disbanding of the Du Bois Clubs.

A well-known professor specialising in Feminist Critical Race & Ethnic Studies at the University of California, Santa Cruz named Bettina Aptheker was a delegate to the June 1964 founding convention of the W.E.B. DuBois Clubs.
Moorfield Storey
Storey was a prominent constitutional lawyer, past president of the American Bar Association and the first President of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP), from its founding in 1909 until he died in 1929. Storey prosecuted the NAACP’s early Supreme Court victories. He was later aided by Louis Marshall (1856-1929), another known constitutional lawyer and Jewish communal leader.
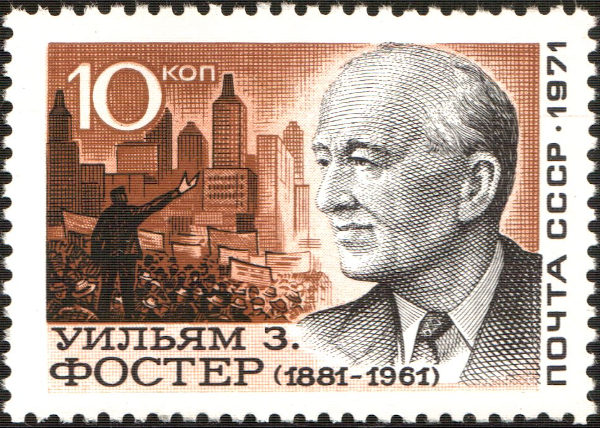
“By 1922, the Communists in America had received their orders from the Communist International to exploit Negroes in the Communist program against the peace and security of the United States. In 1923, the NAACP began to receive grants from the Garland Fund, which was a major source for the financing of Communist Party enterprises. Officials of the Fund included Communists William Z. Foster, Benjamin Gitlow, Elizabeth Gurley Flynn, Scott Nearing, and Robert W. Dunn, along with prominent leftwingers Roger Baldwin, Sidney Hillman, Ernest Gruening, Morris Ernst, Mary E. McDowell, Harry F. Ward, Judah L. Magnes, Freda Kirchwey, Emanuel Celler, Paul H. Douglas, Moorfield Storey, and Oswald Garrison Vilard). The grants continued until, at least, 1934”.
From 1905 until its dissolution in 1921 Storey was president of the national Anti-Imperialist League; an echo chamber of Comintern's World Anti-Imperialist League.
Robert Franklin Williams
President of the Monroe, North Carolina chapter of the NAACP in the 1950s and into 1961. Williams identified as a Black Nationalist and lived in both Cuba and The People's Republic of China during his exile between 1961 and 1969. Williams went to Cuba in 1961 by way of Canada and Mexico. He regularly broadcast addresses from Cuba to Southern blacks on “Radio Free Dixie”. He established the station with approval of Cuban President Fidel Castro, along with the assistance of the Cuban citizens, and operated it from 1962 to 1965.
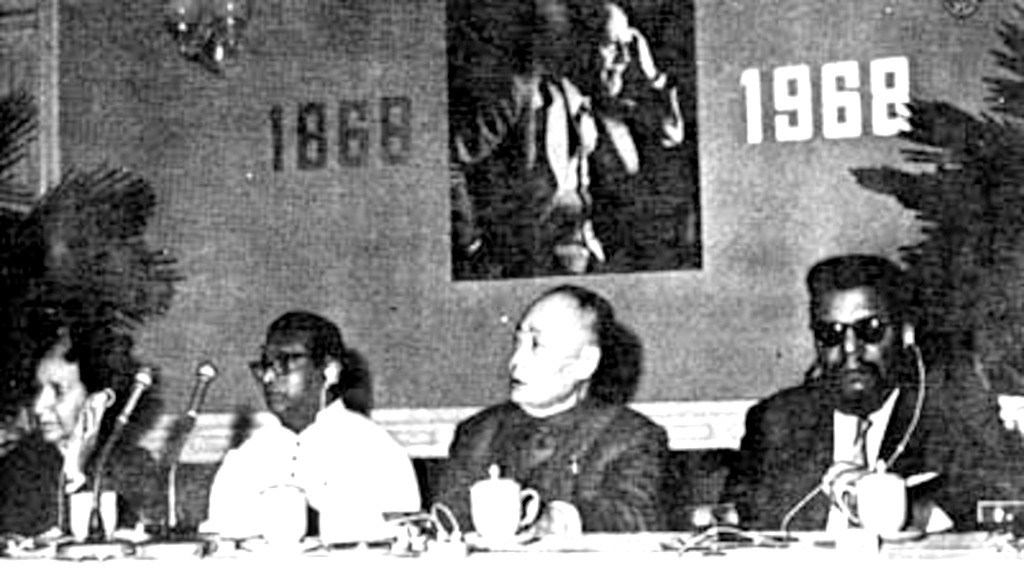

Williams’s flight to Cuba partly inspired the creation of RAM. In Ohio around 1961, black members of Students for a Democratic Society, as well as activists in the Student Non-violent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) and the Congress of Racial Equality (CORE), met in a small group to discuss the significance of Williams’s work in Monroe and his subsequent exile.
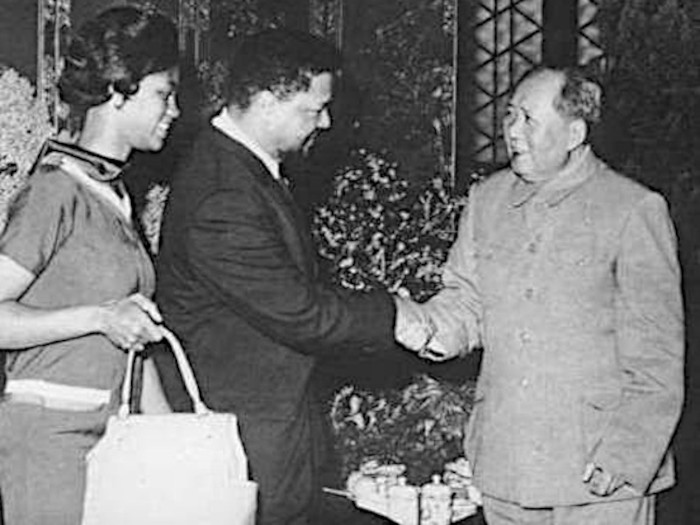
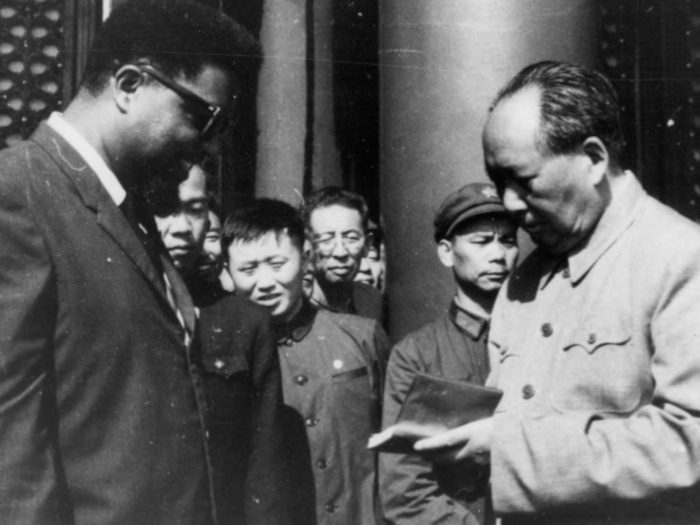


In 1965, Williams and his wife left Cuba to settle in China, where he was well received. They lived comfortably there, and he associated with higher functionaries of the Chinese government. Also in 1965, Williams travelled to Hanoi, then the capital of North Vietnam. In a public speech, he advocated armed violence against the United States during the Vietnam War, congratulated China on obtaining its nuclear weapons (which Williams referred to as “The Freedom Bomb”), and showed his solidarity with the North Vietnamese against the United States military onslaught of the country. As an exiled revolutionary in China during its most tumultuous era, Williams nevertheless predicted that urban rebellions in America’s ghettoes would transform the country.

Williams was suspected by the Justice Department of wanting to fill the vacuum with influence left after the assassinations of his friends Malcolm X and Martin Luther King, Jr. Hoover received reports that blacks looked to Williams as a figure similar to John Brown, the militant abolitionist who attacked a federal facility at Harper's Ferry before the American Civil War. Williams' attempts to contact the U.S. government to return were consistently rebuffed.
Henry Moskowitz
Henry Moskowitz was born on September 27, 1880, in Huși, Romania. He was Jewish. He migrated to the United States in 1883. He attended the New York City public schools and then graduated from the City College of New York in 1899. In 1906, he earned a Ph.D. in philosophy from the University of Erlangen in Germany. Moskowitz was a civil rights activist, and one of the co-founders of the NAACP.
“Moskowitz’s involvement in the NAACP was indicative of early Jewish support; Lillian Wald, Rabbi Emil G. Hirsh, and Rabbi Stephen S. Wise were also founders. The Spingarn brothers served as officers, and Jacob Schiff, Julius Rosenwald, and Herbert Lehman contributed funds.”.
In 2010, the Square of Hope in the Garden of the Righteous Among the Nations at Yad Vashem was dedicated in his honor. He was also a supporter of the Givat Haviva Educational Institute in Israel and the USC Shoah Foundation Institute for Visual History and Education. In 1998, he was recognised by former Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu with the Foreign Investor Jubilee Award. Although raised Hassidic, after World War II, he practiced Modern Orthodox Judaism.
Spingarn Brothers
Arthur Spingarn
In January 1911, the NAACP organised its first branch in Harlem, New York with the help of Joel Spingarn, who persuaded his brother, Arthur (1878–1971) and Charles H. Studin, Arthur’s law partner, to join him. The branch established a vigilance committee, which became the National Legal Committee, to deal “with injustice in the courts as it affects the Negro.” Arthur served as the chairman of the National Legal Committee until 1939 and as NAACP president from 1939 to 1966. The members of the Legal Committee also included Clarence Darrow, Felix Frankfurter, and Charles Houston.
Joel Elias Spingarn
Joel Elias Spingarn (1875-1939) was born in New York City to an upper middle-class Jewish family. Joel was chairman of Comparative Literature at Columbia University, and was the eldest son of an Austrian Jewish tobacco merchant. He served as professor of comparative literature at Columbia University from 1899 to 1911. His academic publishing established him as one of America's foremost comparativists.
Oswald Garrison Villard
Villard funded the NAACP’s budget and provided free office space in the Evening Post building. He resigned as NAACP chairman in 1914 due to irreconcilable differences with W. E. B. Du Bois, but remained a board member of the NAACP until he died in 1949. Villard originally supported Booker T. Washington (Prince Hall Freemasonry), believing education was the solution to the “Negro problem,” but the Brownsville affair and Atlanta riot convinced him of the need for a more militant strategy. The “Committee for the Advancement of the Negro Race” (1906) he envisioned became the blueprint for the NAACP.
Miscegenation Melting Pot
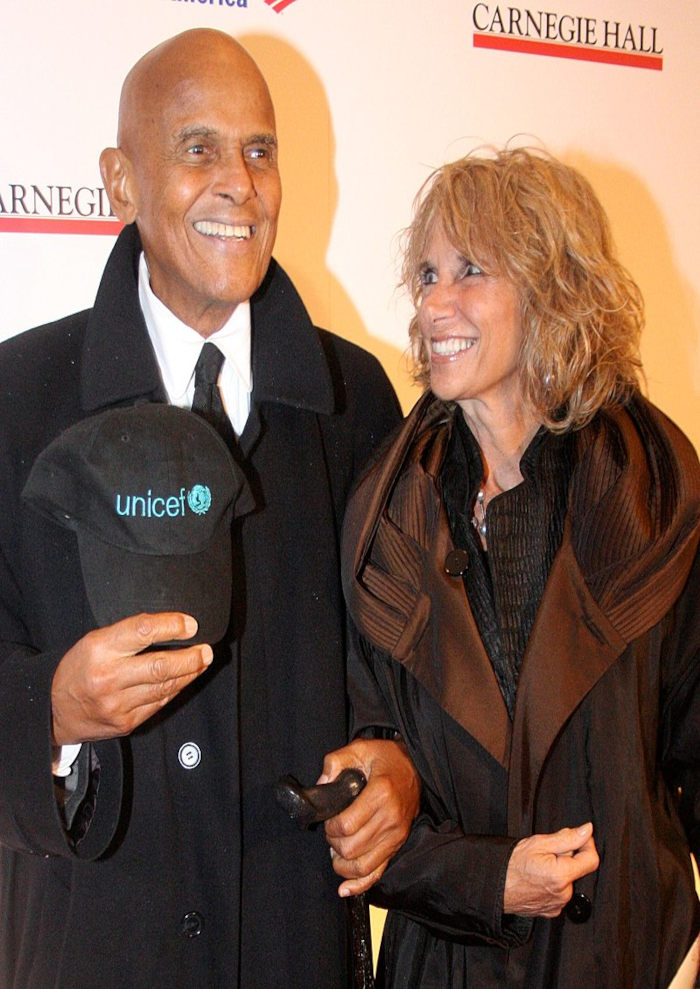
Communism and Martinism pushed the NAACP into a miscegenation agenda and since then many Springarn medalists [including satanist Sammy Davis Jr and Harry Belafonte] have entered inter-racial partnerships birthing race mixed families. There is also the bizzare transracial agenda of Rachael Dolezal, ex-president of the NAACP chapter in Spokane, Washington, from 2014 until June 2015. Dolezal was a white women, of European descent, pretending to be a Black Afro-American woman.
Rachael Dolezal
Rachael Dolezal (born Rachel Anne Dolezal, as a blonde blue-eyed baby) was president of the NAACP chapter in Spokane, Washington, from 2014 until June 2015, before she resigned amid controversy over her true racial identity. Dolezal received public scrutiny when her white parents publicly stated that she was passing as black. The statement by Dolezal's parents (who are white and primarily of German, Czech, and Swedish origin) followed Dolezal's reports to police and local news media that she had been the victim of race-related hate crimes; however, a subsequent police investigation had failed to substantiate her allegations. Dolezal is of European ancestry and has no verifiable African ancestry.
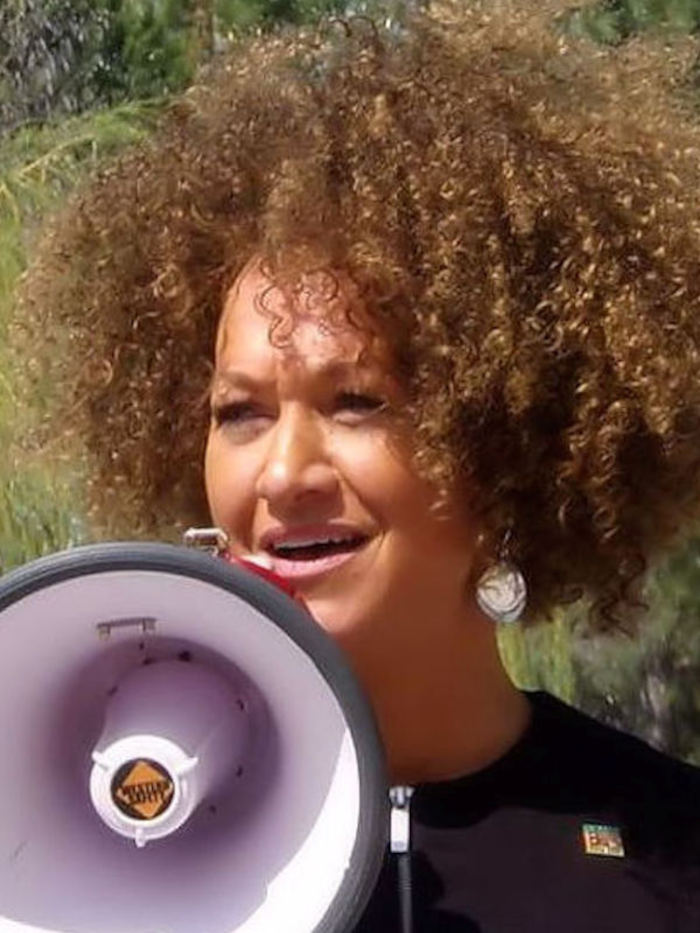
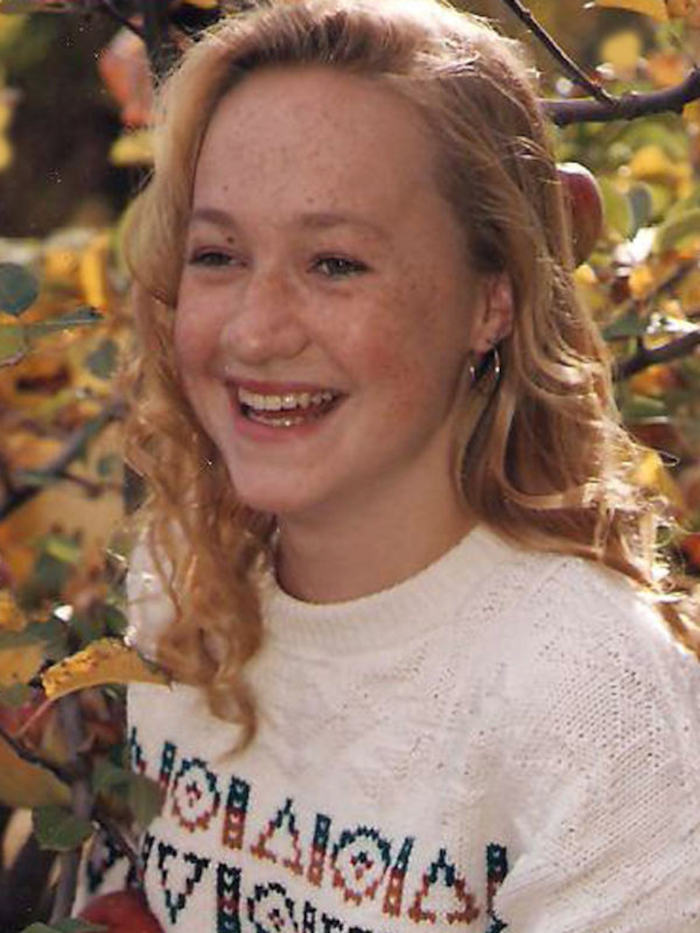

According to her brother, Ezra, Dolezal began changing her appearance as early as 2009, when she began using hair products that she had seen Ezra's biological sister use. She began darkening her skin and perming her hair sometime around 2011. When Ezra moved in with Rachel in 2012, she told him that Spokane-area residents knew her as black and said, “Don't blow my cover”. Dolezal's uncle, Dan Dolezal, has stated that his niece first claimed that a black friend named Albert Wilkerson was her real father in 2012 or 2013. In another 2015 interview, Dolezal referred to her “stepfather”. Dolezal's mother has said she has never met Albert Wilkerson and that Dolezal does not have a stepfather.
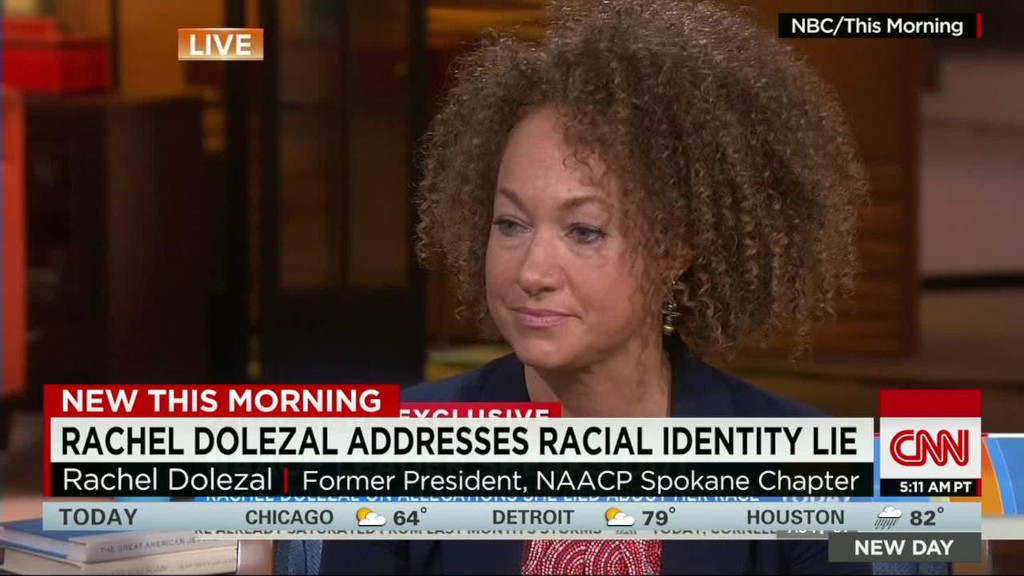
After the controversy regarding Dolezal's racial identity became public, the NAACP released a statement supporting her leadership. However, a petition calling for her to resign her position as President of the Spokane chapter of the NAACP was launched. Dolezal stepped down from her position at the NAACP on June 15, 2015.
The NAACP has received funding from the AT&T Foundation, the Bauman Family Foundation, the Carnegie Corporation of New York, the Annie E. Casey Foundation, the Freddie Mac Foundation, the Ford Foundation, the Bill, and Melinda Gates Foundation, the JEHT Foundation, the Joyce Foundation, the W.K. Kellogg Foundation, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, the Open Society Institute, the David, and Lucile Packard Foundation, the Rockefeller Foundation, the Sara Lee Foundation, the Scherman Foundation, the Verizon Foundation, the Tides Foundation and Boeing.
Desegregation Busing
In the 1960s, civil rights lawyers from the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) filed lawsuits on behalf of black parents and children requesting the courts to require desegregation plans for individual cities. In a 1969 decision, Alexander v. Holmes County Board of Education, the Supreme Court indicated that it would no longer tolerate delays in school desegregation.
In 1965, NAACP attorney Julius LeVonne Chambers (1936–) initiated a lawsuit to end racial segregation in the Charlotte public schools.
“We must realise that our party's most powerful weapon is racial tensions. By propounding into the consciousness of the dark races that for centuries they have been oppressed by whites, we can mould them to the program of the Communist Party. In America, we will aim for a subtle victory. While inflaming the Negro minority against the whites, we will endeavour to instil in the whites a guilt complex for their exploitation of the Negroes. We will aid the Negroes to rise in prominence in every walk of life, in the professions and in the world of sports and entertainment. With this prestige, the Negro will be able to intermarry with the whites and begin a process which will deliver America to our cause.”.